Key Takeaways
- Salesforce security in 2026 centers on OAuth-based supply chain attacks, social engineering, and AI-driven threats, which require stronger controls than platform defaults alone.
- Compliance expectations around GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and emerging AI regulation make structured data governance in Salesforce a core operational requirement, not an optional add-on.
- Modern security programs tie DevSecOps practices, continuous monitoring, and Zero Trust principles together to reduce breach risk and clarify the financial ROI of security investments.
- Bridging gaps between Salesforce admins, RevOps, and security leaders improves permissions design, logging, and incident response, reducing internal misconfiguration risk.
- Coffee helps Salesforce teams automate data capture, enrichment, and activity logging, supporting accurate, compliant CRM data; get started with Coffee to improve data integrity with less manual work.
The Evolving Threat Landscape: Why Salesforce Security Needs Executive Attention
Salesforce now sits at the center of revenue operations, customer data, and AI workflows, which makes the platform a high-value target for attackers and a focal point for regulators.
OAuth Supply Chain Attacks and Social Engineering Risks
Attackers expanded their focus in 2025 with three major OAuth-based supply chain attacks affecting 100+ enterprises, including Google, Chanel, Qantas, LVMH, Cisco, and Pandora. Malicious apps impersonated tools such as Data Loader, abused stolen tokens, or took over ISV tenants to obtain long-lived refresh tokens that bypassed traditional authentication.
The same period showed how voice phishing, combined with social engineering, could convince users to install these apps. Effective Salesforce security now depends on both technical controls and consistent user education.
Internal Risks: Misconfigurations, Ghost Sites, and Over-Permissioning
Internal configuration errors create large, persistent attack surfaces. Common risks include complex permission models, sensitive data misconfigurations, and abandoned Experience Cloud sites that still expose data.
A major weakness comes from the disconnect between Salesforce administrators and security teams. Over-permissioned users and liberal default settings magnify these issues, turning minor configuration oversights into serious exposure.
AI-Driven Threats and the Shift Toward Zero Trust
Security leaders expect AI to shape both attacks and defenses. An estimated 97% of cybersecurity experts expect AI-generated incidents to become a dominant threat vector. Within Salesforce, AI Agents can leak sensitive data through indirect prompt injection when safeguards are weak.
To respond, about 40% of organizations plan to implement Zero Trust frameworks by 2026. These programs emphasize continuous verification, least-privilege access, and strong identity controls, rather than relying on network location or role alone.
Salesforce Compliance Frameworks and Practical Data Protection
What Regulations Mean for Salesforce Configuration
GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, SOX, PCI DSS, and emerging AI rules all impact how teams configure Salesforce. GDPR stresses consent, data minimization, and rights to access or delete data. CCPA emphasizes transparency and opt-out controls. HIPAA demands strict access management, encryption, and auditable records for protected health information.
Across these frameworks, recurring themes include:
- Clear data inventories and purpose-specific processing
- Strong access controls and least-privilege permissions
- Consistent logging and auditable change histories
- Defined processes for data subject or patient requests
Data Protection Strategies That Matter Most in Salesforce
The following controls give Salesforce leaders the most immediate security and compliance impact.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA functions as a foundational safeguard against credential theft and OAuth token abuse, which became more visible in 2025.
- Connected app governance: Teams should enforce Connected App restrictions and audit ISV or AppExchange apps for suspicious OAuth patterns. Salesforce’s 2025 requirement for admin approval helps, but full app lifecycle governance remains necessary.
- Logging and monitoring: EventLogFiles on the free tier persist for only 24 hours. Exporting logs automatically and analyzing behavior rather than just authentication outcomes reduces blind spots.
- Permissions and permission sets: With permissions on profiles slated for retirement by 2026, organizations benefit from early adoption of permission-set-based models that offer finer control and clearer audits.
- Security Health Check cadence: Security Health Checks that target scores of 90% or higher work best as recurring controls. Regular scheduling keeps pace with new apps, fields, and business processes.
Building a Secure, Compliant Salesforce Operating Model
Integrating DevSecOps into Salesforce Delivery
DevSecOps alignment brings security testing and policy checks into the CI/CD pipeline rather than waiting for manual reviews. This shift matters because about 81% of Salesforce teams now use CI/CD practices.
Teams that embed static and dynamic scanning, configuration checks, and automated approvals into their pipelines typically see faster detection, lower remediation costs, and smoother audits.
Quantifying the Business Impact of Strong Security
The economic risk is substantial. Organizations lose an estimated $40 billion each year to AI-driven cyberattacks, in addition to fines, legal fees, and loss of customer confidence.
Positioning Salesforce security spending as revenue protection clarifies the return on investment. Benefits include fewer critical incidents, more predictable audit cycles, lower cyber insurance premiums, and stronger customer trust in how data is handled.
Closing the Gap Between Admin and Security Teams
Effective programs bring Salesforce admins, security leaders, RevOps, and sales leadership into a shared operating rhythm. Cross-functional governance can include:
- Joint security and configuration reviews for new objects, fields, and apps
- Shared dashboards tracking login anomalies, permission changes, and failed MFA attempts
- Regular training where admins explain platform behavior and security teams share current threats
These habits reduce misconfigurations and ensure faster, more coordinated responses when incidents occur.
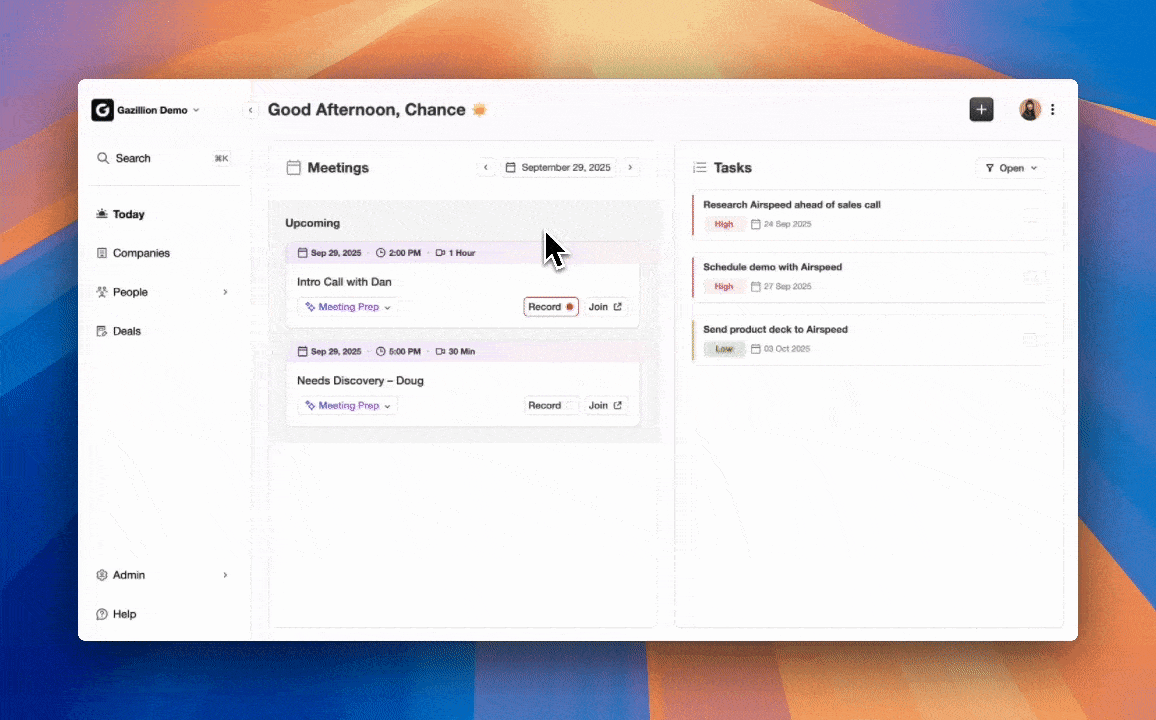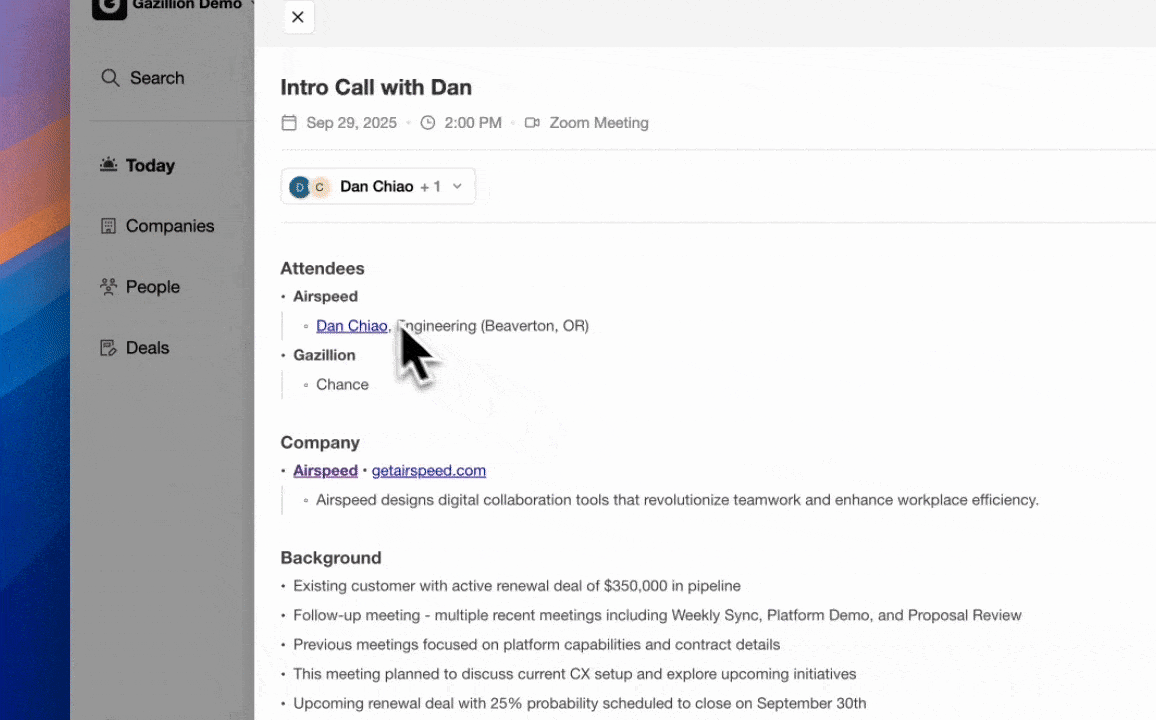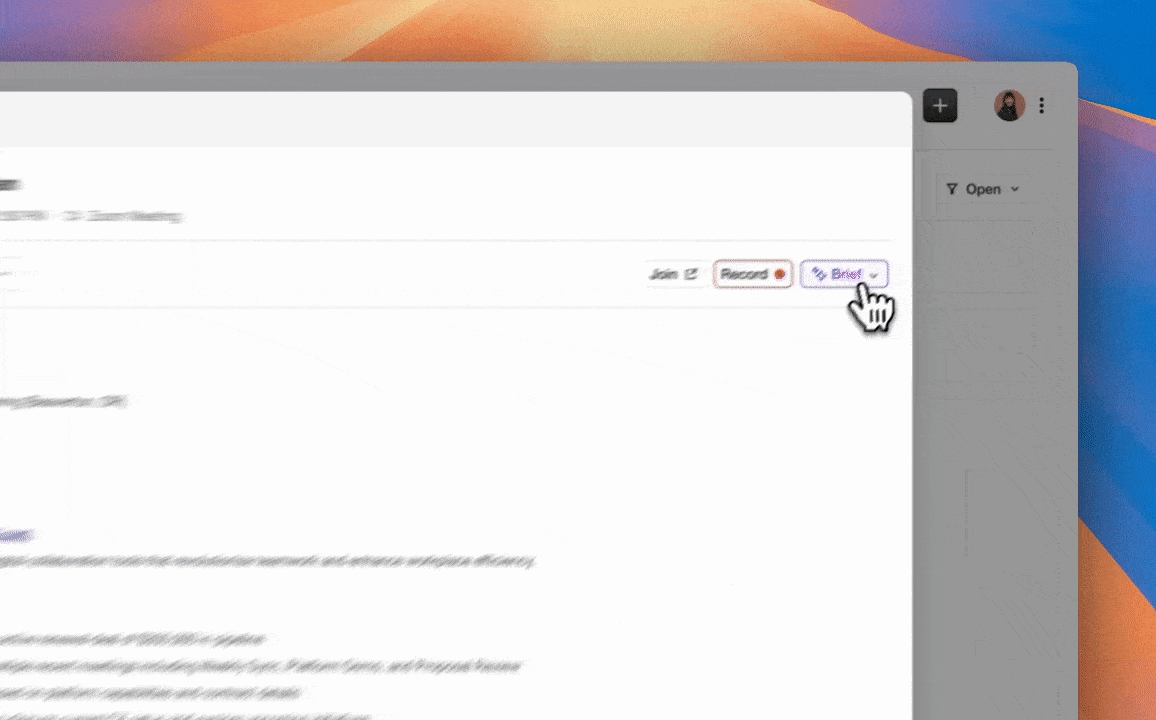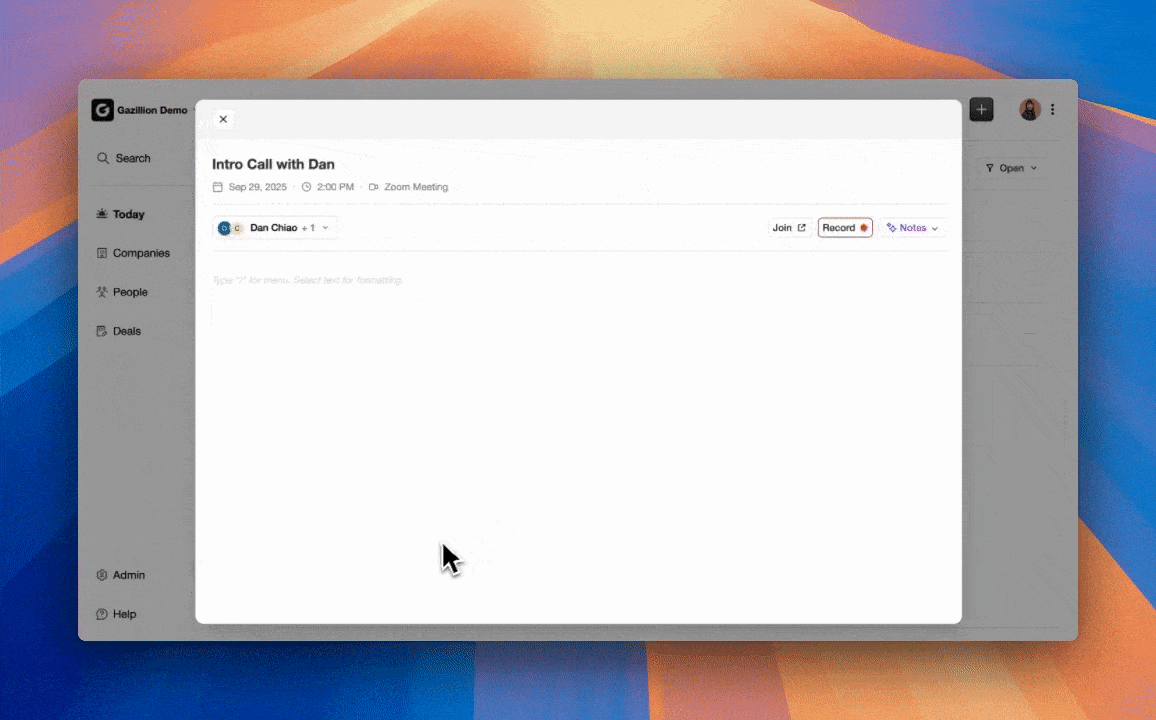
Using Coffee to Support Salesforce Data Integrity and Compliance
Coffee focuses on the quality and completeness of data entering Salesforce, which directly supports both security and compliance efforts.
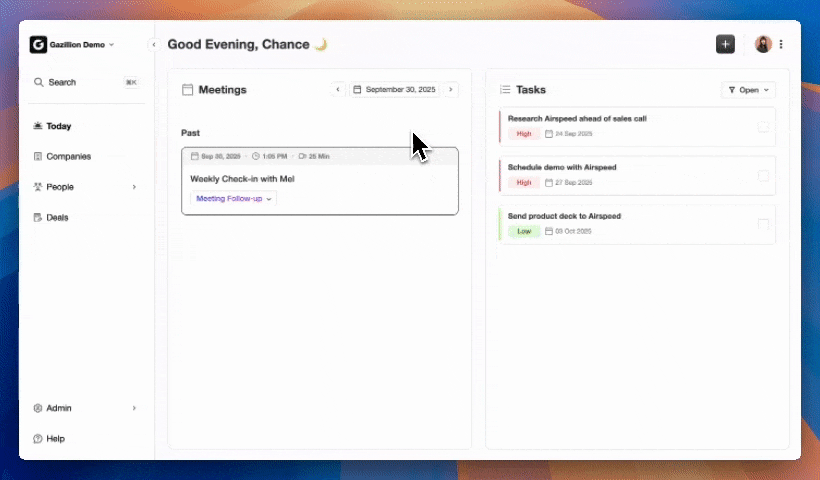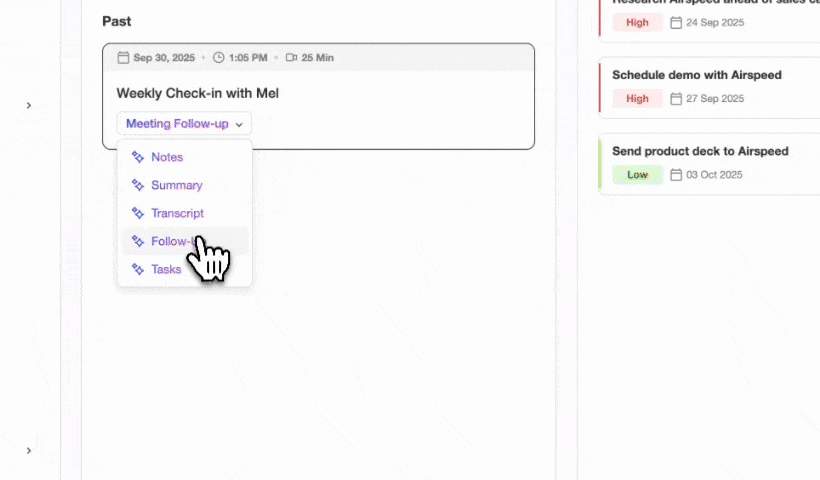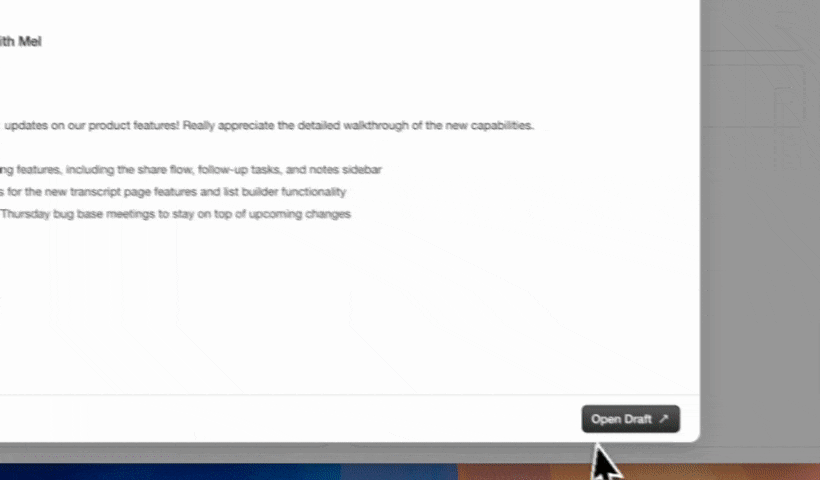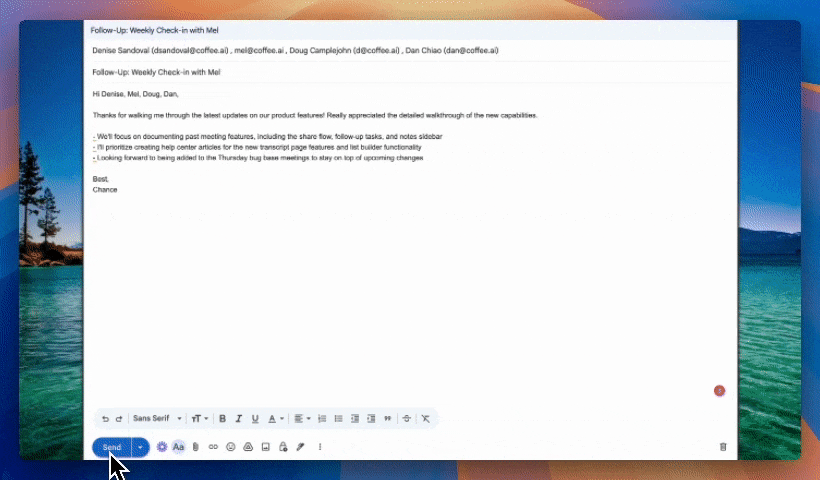
Automated Data Entry and Enrichment
The Coffee Agent creates and enriches contacts and accounts based on real interactions, so teams no longer depend on manual data entry. Salespeople often report spending large portions of their week on CRM updates; automation returns that time to selling and reduces incomplete or inconsistent records.
Accurate, timely data reduces compliance risk by ensuring that consent details, communication history, and key attributes are captured and auditable.
Continuous Activity Logging for Better Audit Trails
Coffee automatically logs fields such as last activity and next activity, giving teams a clear, current picture of account engagement. This supports auditability for regulations that expect traceable histories of customer and patient interactions.
Sales and RevOps leaders gain reliable reports without asking reps to remember every update, which improves both forecasting and governance.
Simplifying the Salesforce Data Tool Stack
Coffee consolidates functions that often require multiple point solutions, such as enrichment, capture, and engagement tracking. This consolidation reduces integration complexity and limits additional OAuth entry points.
|
Feature |
Coffee Agent |
Traditional Approach |
|
Data capture |
Automated from meetings and outreach |
Manual CRM updates |
|
Data quality |
Consistent enrichment and normalization |
Variable formats and gaps |
|
Audit readiness |
Structured activity histories |
Patchy, user-dependent logging |
Teams that want stronger Salesforce data foundations can get started with Coffee to automate core CRM hygiene work.
Readiness, Common Pitfalls, and Next Steps for 2026
Assessing Salesforce Security Maturity
Most organizations fall into three stages of Salesforce security maturity:
- Reactive: Focus on basic configuration and incident response after issues occur
- Proactive: Use structured monitoring, access reviews, and change control
- Optimized: Apply automation, behavioral analytics, and integrated threat intelligence
Identifying your current stage helps prioritize projects such as MFA rollout, permission redesign, log centralization, and Zero Trust planning.
Avoiding Strategic Missteps
Even experienced teams face recurring pitfalls, including:
- Over-relying on Salesforce default profiles that grant broad object access
- Missing the 24-hour EventLogFiles window for critical security data
- Treating Security Health Checks as one-time events instead of recurring controls
- Underestimating social engineering and failing to refresh security awareness training
- Overlooking both the risks and defensive potential of AI in security programs

Frequently Asked Questions about Salesforce Security and Compliance
How can organizations reduce the risk of OAuth-based supply chain attacks in Salesforce?
Effective defenses include universal MFA, strict Connected App approval and review, automated export of security logs before they expire, high Security Health Check standards, and regular audits of ISV and AppExchange integrations for unusual OAuth patterns.
What internal factors most often weaken Salesforce security?
Key internal risks include over-permissioned roles, complex sharing rules that few people fully understand, abandoned Experience Cloud sites that still expose data, and gaps in communication between Salesforce admins and security teams.
How will the retirement of permissions on profiles by 2026 affect access control?
The shift away from profile-based permissions pushes organizations toward permission sets and permission set groups. Early planning and structured role design reduce disruption and create clearer, more auditable access models.
Can AI safely support Salesforce security and compliance?
AI can strengthen defenses by analyzing behavior, highlighting anomalies, and automating repetitive checks. At the same time, AI components need their own guardrails to prevent prompt injection, data leakage, and unapproved access paths.
Conclusion: Turning Salesforce into a Secure, Well-Governed System of Record
Salesforce security and compliance in 2026 require more than basic configuration. Leaders need structured governance, strong identity controls, reliable logging, and closer collaboration across admin, RevOps, and security teams.
Coffee complements these efforts by improving the accuracy and completeness of Salesforce data through automated capture, enrichment, and activity logging. This support gives organizations cleaner audit trails and reduces the manual work that often leads to gaps.
Teams that want a stronger Salesforce data foundation can get started with Coffee to combine secure processes with consistent, high-quality CRM data.
