Key Takeaways
- Proactive CRM automation platforms in 2026 shift CRMs from passive databases into active systems that capture data, manage meetings, and surface insights without constant human input.
- Legacy CRMs struggle with manual data entry, low adoption, and poor data quality, which leads to inaccurate forecasting and missed revenue opportunities.
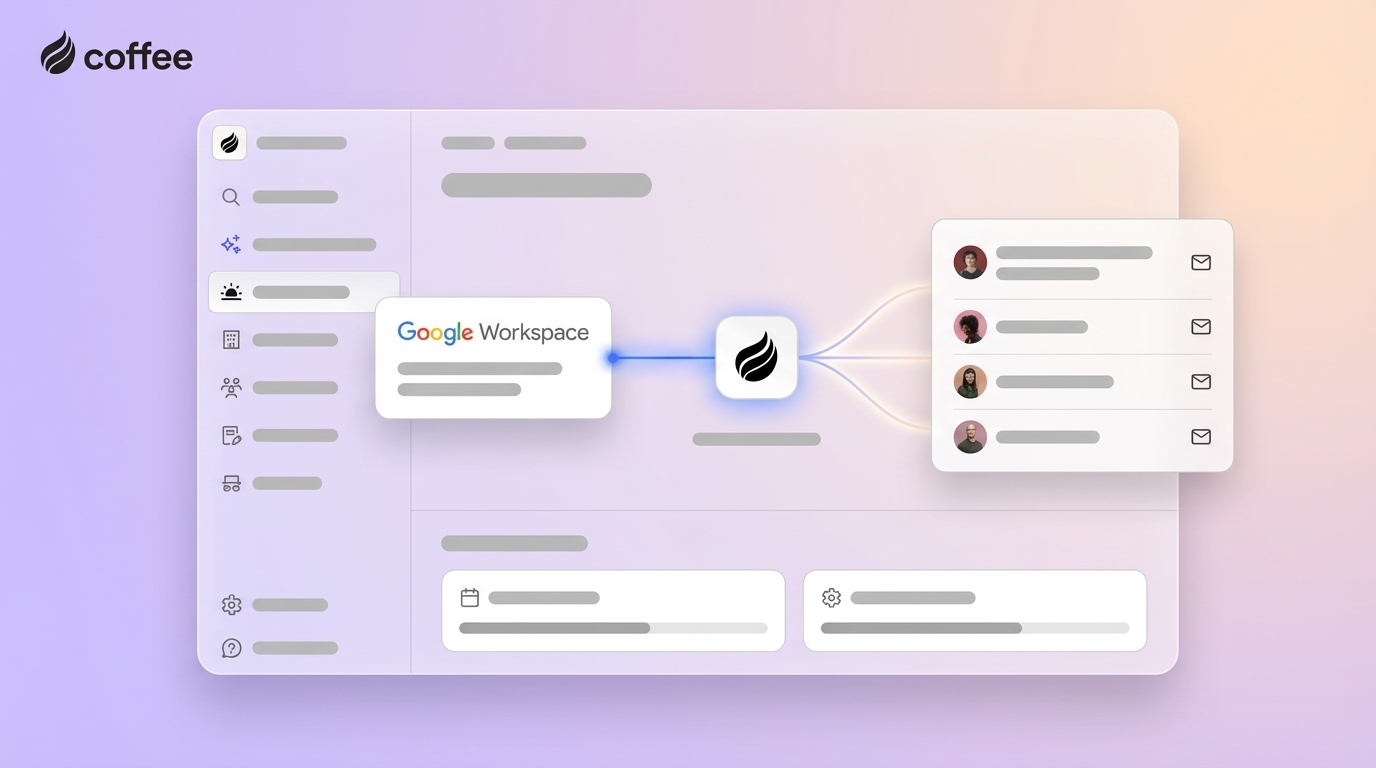
- Agent-led platforms like Coffee focus on data quality by collecting information directly from emails, calendars, and calls, so sales teams spend more time selling and less time on admin work.
- Successful adoption of proactive CRM automation depends on clear ROI goals, alignment across revenue operations, sales, and IT, and a preference for unified platforms over disconnected point tools.
- Teams that want to automate data entry, meeting workflows, and pipeline insights can explore Coffee’s pricing and plans at Coffee.
Beyond Reactivity: What Defines a Proactive CRM Automation Platform in 2026?
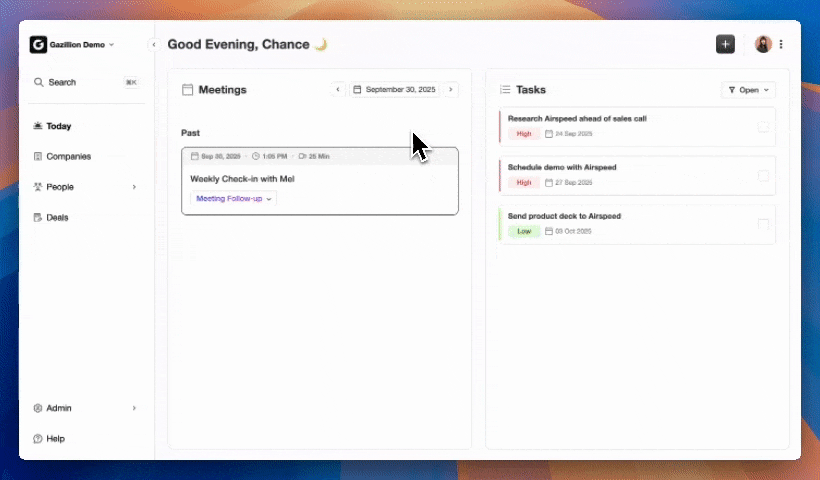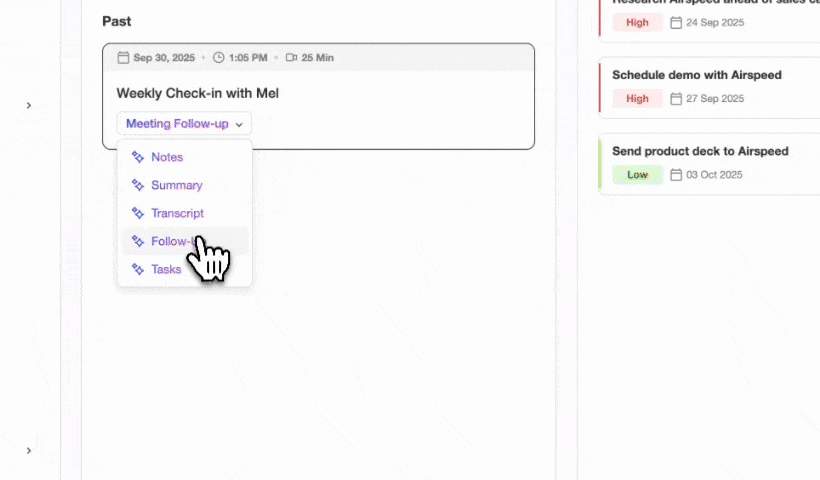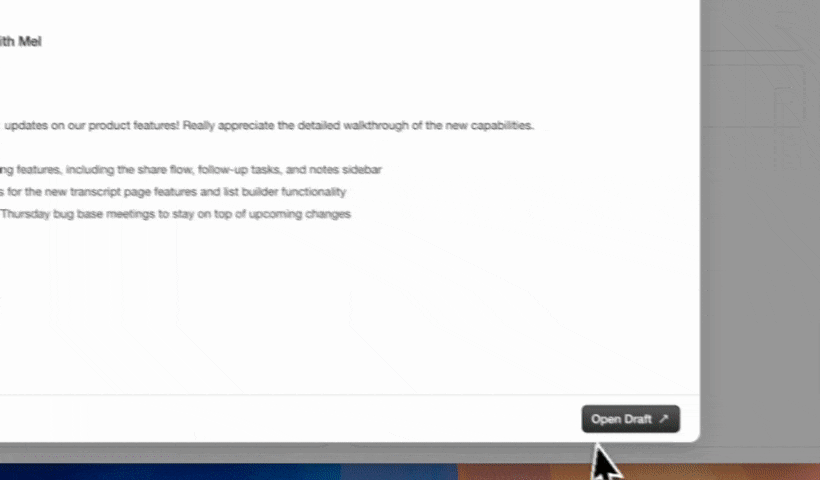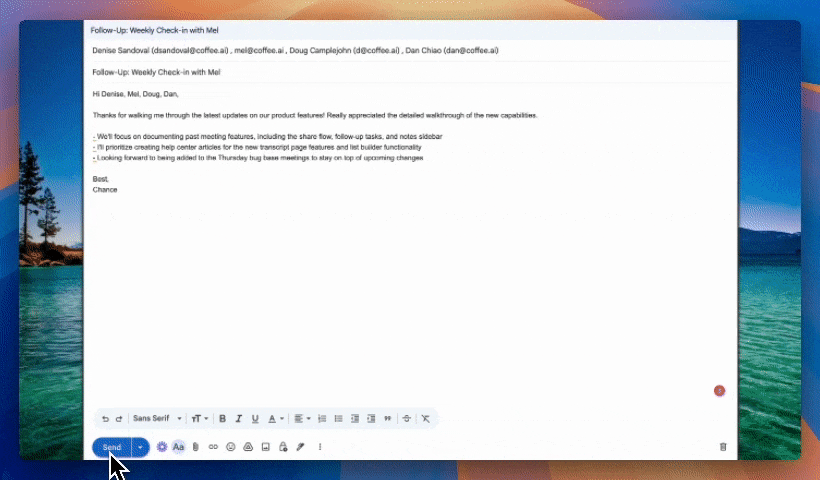
Proactive CRM automation platforms operate as active participants in sales operations rather than static record systems. These platforms rely on intelligent agents that capture data, manage workflows, and suggest next steps, so the CRM contributes to outcomes instead of only recording activity.
In 2026, AI capabilities allow CRMs to interpret conversations, structure information, and update records in real time. Sales teams gain current, trustworthy data without extra manual work.
Key Characteristics of Proactive Automation
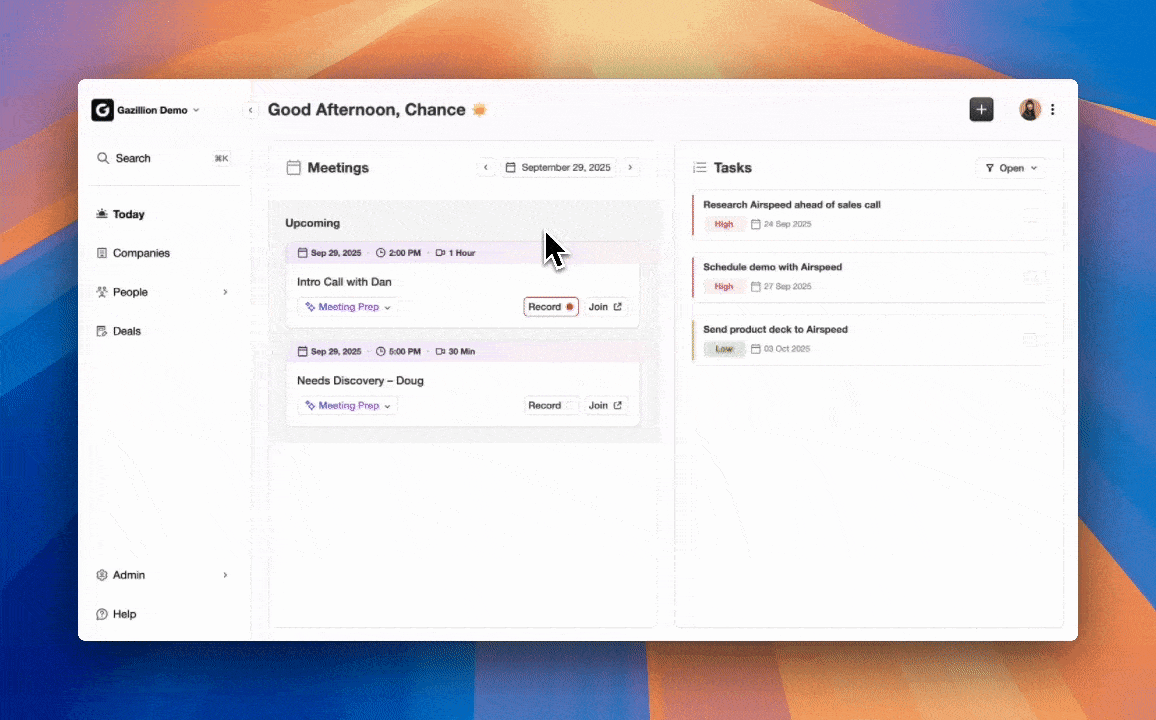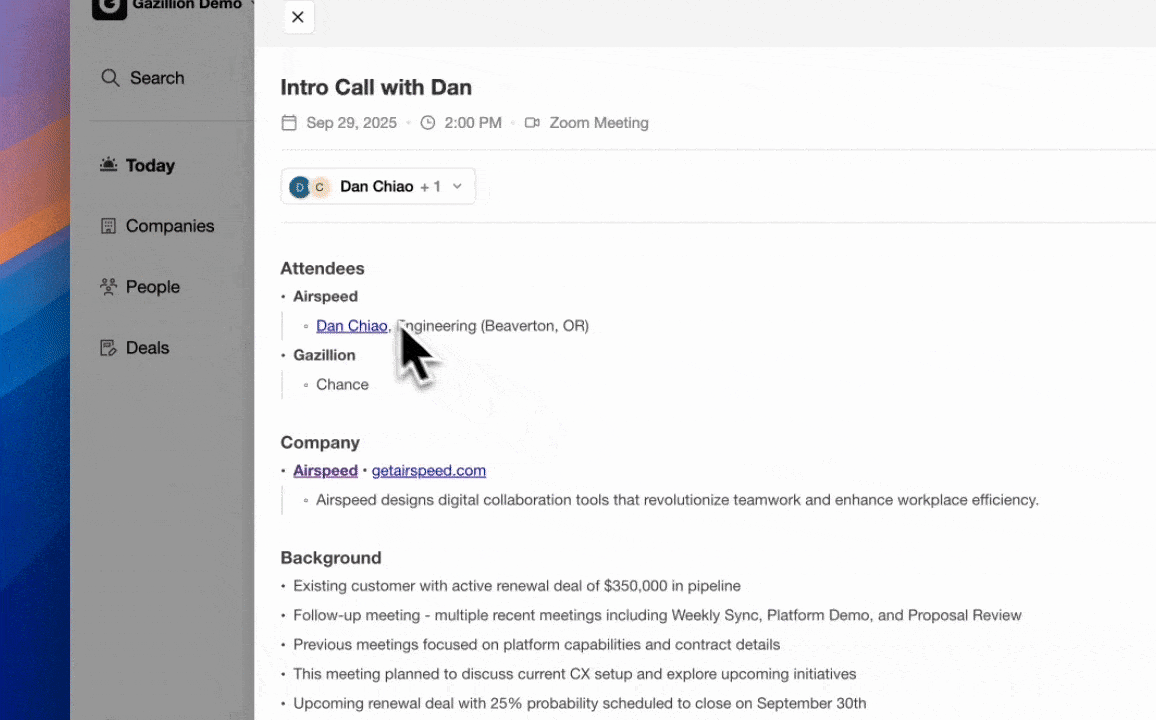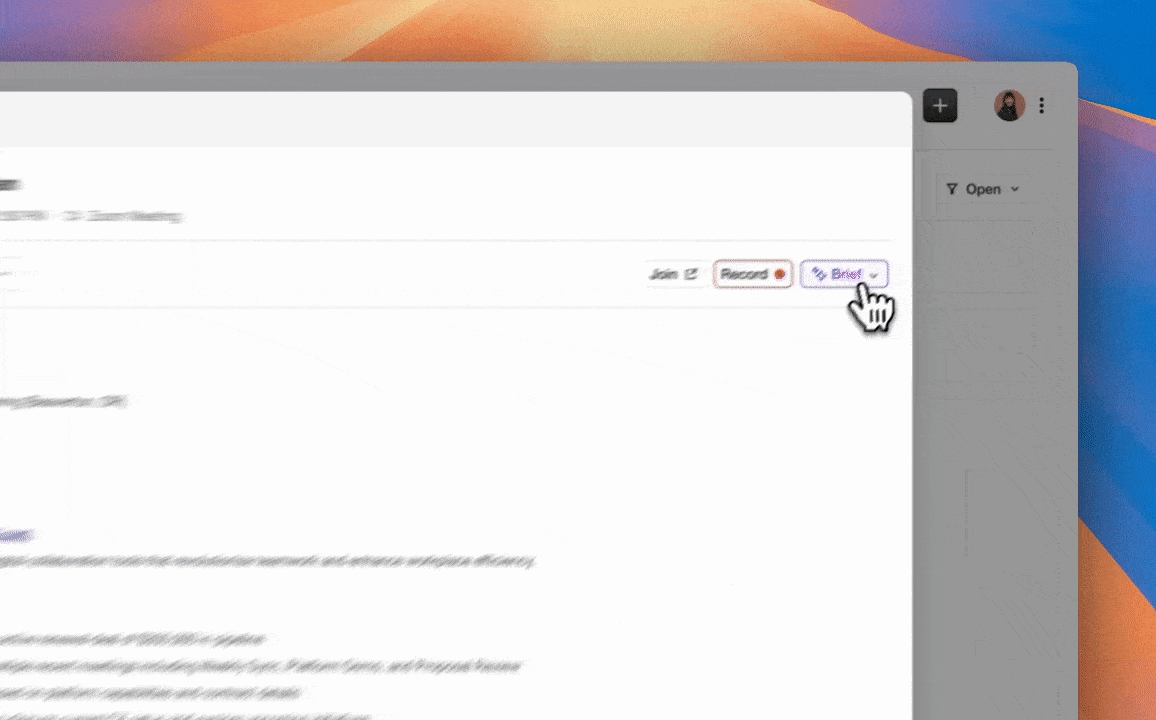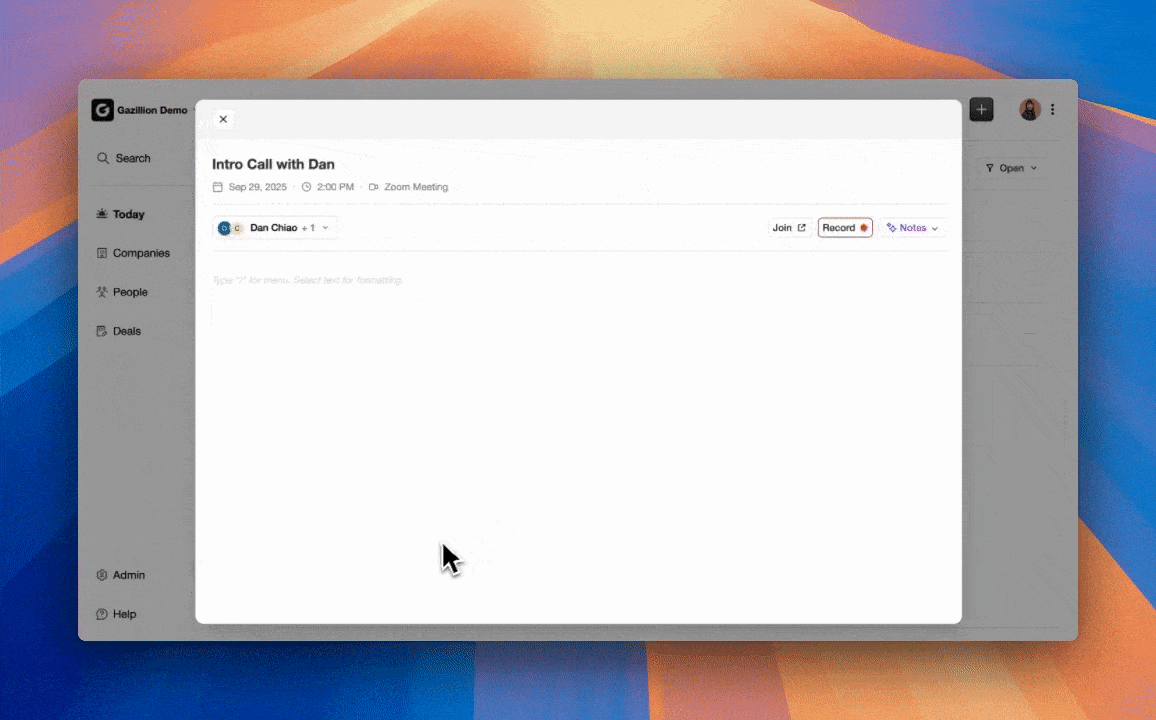
Modern proactive CRM platforms typically share four core capabilities.
- Automated data capture and enrichment from emails, calendars, calls, and transcripts.
- AI-supported meeting management with briefing docs, summaries, and follow-up drafts.
- Pipeline intelligence that tracks changes, risks, and momentum without manual reporting.
- Consolidation of tools for enrichment, recording, and forecasting into one environment.
These functions move CRMs from reactive data storage toward practical systems that guide sales decisions.
The Critical Flaws of Legacy CRMs: Why Proactivity Is Non-Negotiable
Legacy CRMs rely on people to remember to log every interaction. That model produces incomplete data, low adoption, and constant friction between sales teams and operations.
The core issue is human-dependent data entry. Sales representatives often spend most of their time on administrative work instead of selling, which leaves records incomplete and out of date. Inconsistent data leads to weak forecasts, slow responses to customer signals, and difficult handoffs between teams.
As competition intensifies in 2026, teams that continue to rely on manual updates risk operating on partial information while competitors use automated, high-quality data to make faster decisions.
Coffee: The Agent-Led Approach to Proactive CRM Automation
Coffee treats CRM as an always-on agent that works alongside the sales team. Instead of asking sellers to feed the CRM, Coffee’s Agent captures and organizes data in the background so representatives can focus on conversations and deals.
Data Quality as the Foundation for Useful AI
Coffee’s philosophy is simple: useful AI requires accurate, complete data. The Agent ingests information directly from emails, calendars, and meeting transcripts, then structures it into contacts, companies, and activities. This approach reduces human error and creates a reliable source of truth for every account.
Deployment Models That Match Your Stack
Coffee offers two primary deployment options that match different stages of CRM maturity.
- Standalone AI-first CRM for smaller teams moving beyond spreadsheets, with automatic setup of records and activity tracking.
- Companion app for Salesforce and HubSpot for mid-market and larger organizations that want better data and automation without replacing their existing CRM.
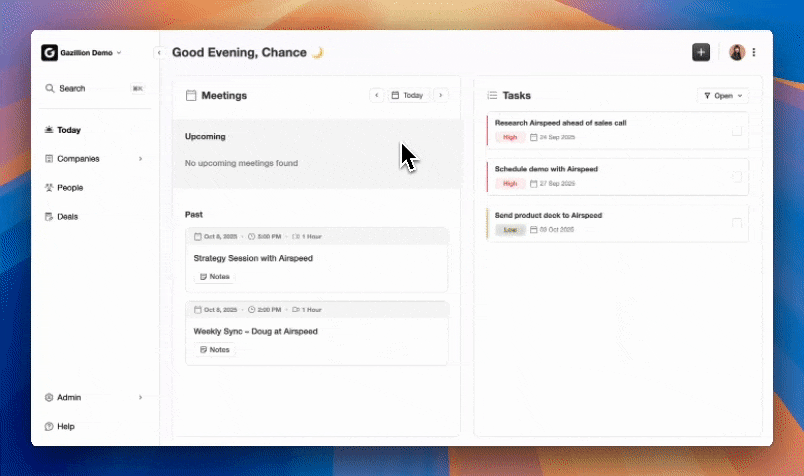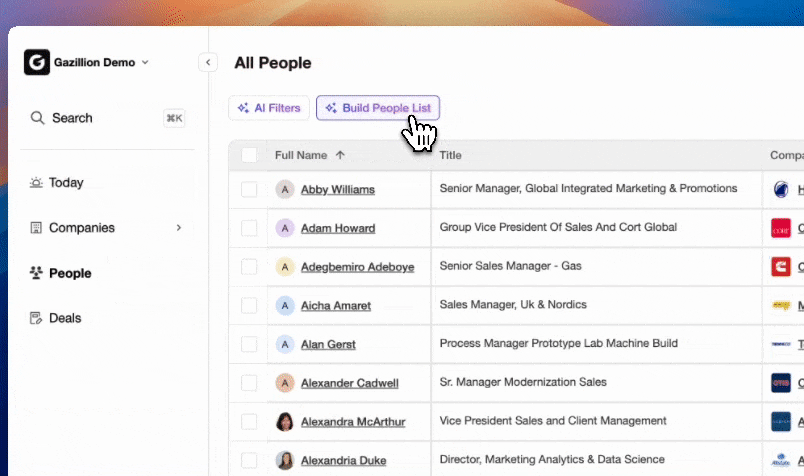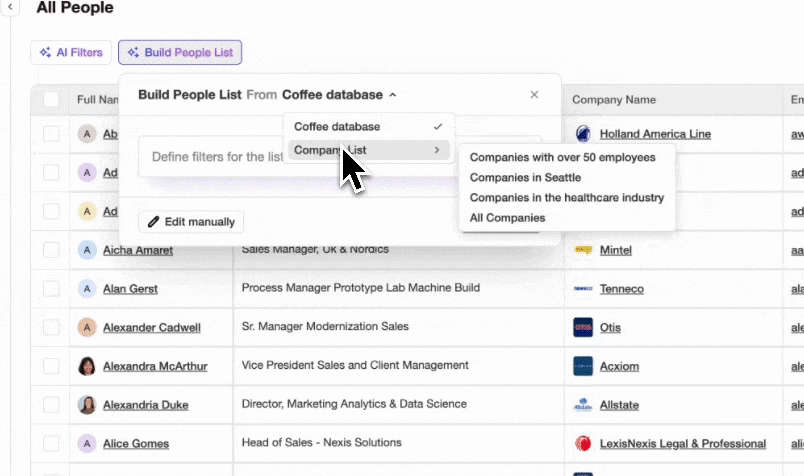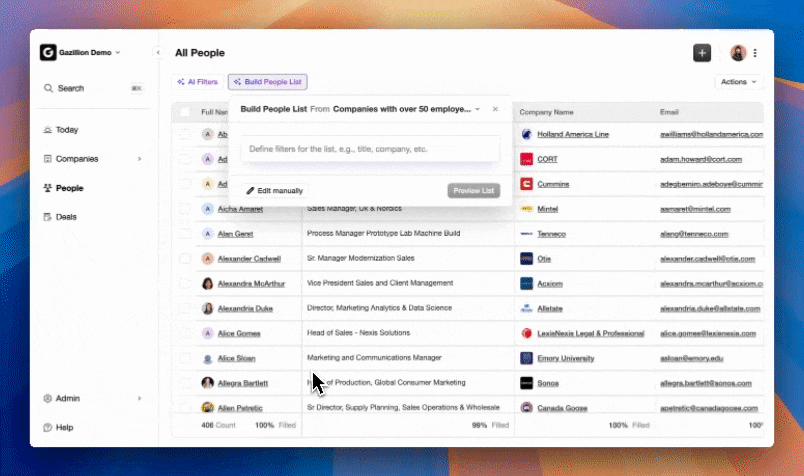
Core Value for Revenue Teams
Coffee’s Agent focuses on five practical outcomes for sales organizations.
- Handles data entry by auto-creating and enriching contacts, companies, and activities, often saving representatives 8 to 12 hours each week.
- Manages meeting workflows with prep briefs, summaries, action items, and follow-up drafts.
- Delivers pipeline intelligence through accurate, automatically updated deal data and week-over-week change tracking.
- Reduces the number of tools needed for enrichment, call recording, and forecasting by centralizing these capabilities.
- Improves rep experience by removing most CRM chores, so the system feels like a practical assistant instead of an obligation.
Explore Coffee pricing and plans to see how an agent-led CRM can fit your current sales process.
Strategic Considerations for Adopting Proactive CRM Automation
Evaluation Framework and Organizational Readiness
Effective implementation starts with a clear view of your current state. Revenue leaders can assess three areas before choosing a platform.
- Data quality: Where are the biggest gaps in contact, activity, and pipeline accuracy?
- Integrations: Which tools and systems must connect to the CRM without disruption?
- Change management: How ready are sales, RevOps, and IT to adjust workflows around automation?
Shared ownership between revenue operations, sales leadership, and IT helps ensure that automation supports real-world processes rather than creating new friction.
Build vs. Buy for AI-Driven Automation
Internal builds offer control but require specialized AI expertise, engineering capacity, and ongoing maintenance. Many teams underestimate the cost of keeping custom automation accurate and secure over time.
Buying a specialized platform like Coffee provides tested agent workflows, rapid deployment, and continuous improvements without adding to the internal engineering backlog.
ROI Expectations and Success Metrics
Clear metrics help teams judge whether proactive CRM automation delivers value. Common measures include:
- Hours per rep per week spent on CRM and admin work before and after rollout.
- Percentage of opportunities with complete contact, activity, and stage data.
- Sales cycle length and win rates across segments.
- Number of tools eliminated or consolidated.
Coffee customers often track administrative time savings in the range of 8 to 12 hours per rep per week, alongside more reliable pipeline data.
Scalability and Integration
Teams need platforms that grow with headcount and complexity while maintaining security. Coffee integrates with Salesforce and HubSpot through authenticated connections and is built with enterprise-grade security and compliance in mind.
The Landscape of Proactive CRM Automation Platforms in 2026
The 2026 CRM market now centers on automation and agents that support daily sales workflows. Proactive platforms no longer compete only on fields and reports but on how much work they remove from sellers and operations teams.
Proactive vs. Legacy CRM: A Comparison
|
Feature |
Coffee (Proactive Agent-Led) |
Traditional CRMs (Reactive) |
|
Data Entry |
Automated, agent-led capture and enrichment |
Manual, reliant on rep updates |
|
Pipeline Analysis |
Automated tracking with trend and change views |
Manual reporting, exports, and spreadsheets |
|
Meeting Management |
AI-generated briefs, summaries, and follow-ups |
Notes and emails drafted by hand |
|
Data Quality |
Structured from ground-truth communications |
Inconsistent, based on partial human input |
Strategic Pitfalls for Experienced Teams in CRM Automation
Experienced revenue teams often face similar challenges when rolling out proactive CRM automation. Anticipating these issues helps avoid rework later.
- Underestimating change management when moving from manual updates to agent-driven workflows.
- Ignoring historical data quality until after deployment, which reduces the value of early insights.
- Treating automation as a feature add-on instead of a shift in how selling and reporting operate day to day.
- Investing in disconnected point tools for enrichment, recording, and forecasting rather than a unified agent-led platform.
- Continuing to rely on manual data entry assumptions instead of designing for full automation from the beginning.
Coffee’s agent-led model addresses these risks by focusing on complete automation of capture, enrichment, and pipeline tracking from the outset.
Conclusion: Moving from Passive Records to Active Revenue Support
Competitive sales teams in 2026 benefit from CRMs that participate in the work rather than simply recording it. Proactive, agent-led platforms reduce manual tasks, increase data quality, and provide clearer visibility into pipeline health.
Coffee illustrates this shift by acting as an autonomous agent that captures data, manages meeting workflows, and keeps pipeline information accurate across systems. Teams that adopt this model give sellers more time with customers and leadership more reliable information for decisions.
Review Coffee’s pricing and deployment options to evaluate whether an agent-led CRM automation approach aligns with your 2026 revenue strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Proactive CRM Automation Platforms
What is a proactive CRM platform, and how does it differ from traditional CRMs?
A proactive CRM platform uses intelligent agents to capture data, update records, and surface insights without waiting for manual input. Traditional CRMs primarily store data that people enter by hand, while proactive systems participate directly in daily sales work.
Can a proactive CRM automate data entry without sacrificing accuracy?
Modern proactive CRMs like Coffee scan emails, calendars, and meeting transcripts to build and enrich records. Structured ingestion reduces typos, missing fields, and inconsistent formatting, so data quality often improves compared with manual entry by busy reps.
How does a proactive CRM like Coffee work with existing Salesforce or HubSpot instances?
Coffee’s Companion App connects to Salesforce or HubSpot and acts as an intelligent layer on top. The Agent captures activities, updates records, and pushes structured data back into the primary CRM, so teams keep their current system of record while gaining automation.
How do proactive CRM platforms address low sales rep adoption?
Proactive platforms reduce the need for reps to log calls, update fields, or write summaries. When the system prepares briefs, drafts follow-ups, and keeps pipeline data current, sellers see direct value in the tool and are more willing to use it as part of their routine.
What ROI can organizations expect from proactive CRM automation?
Organizations that adopt agent-led platforms typically measure ROI through time savings, cleaner data, and improved pipeline visibility. Many Coffee customers report that sales representatives save 8 to 12 hours each week on admin work while leaders gain more accurate forecasts and better deal inspection.